More patients develop deep fungal infections (invasive fungal infections) due to the increased use of immunosuppressive drugs, antibiotics, organ transplants, and medically invasive procedures. Therefore, the use of antifungal drugs is also increasing and the rational use of antifungal drugs has become important.
What are the antifungal drugs for invasive fungal infections?
Antifungal drugs commonly used for invasive fungal infections are systemic antifungal drugs. Among them are:
Echinocandins : Anidulafungin, caspofungin and micafungin.
Polyenes : Amphotericin B and nystatin. Nystatin is mainly used in the treatment of Candida infections of the gastrointestinal tract and its oral absorption is poor.
Triazoles : fluconazole, isavuconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole and voriconazole.
Squalene epoxidase inhibitor : Oral terbinafine is mainly used for superficial fungal infections (such as hair, skin and nails).
Pyrimidines : Flucytosine.
Others : Oral griseofulvin is also mainly used for superficial fungal infections (such as hair, skin and nails).
What is the mechanism of action of antifungal drugs?
1. Fungal cell wall synthesis inhibitor : The main component of fungal cell wall is 1,3-β-gluean. Echinocandin drugs exert antifungal effects mainly by inhibiting the synthesis of 1,3-β-gluean. In addition, since human cells do not have cell walls, the toxicity of echinocandin drugs is relatively low.
2. Membrane Stability Inhibitors : Polyenes bind to ergosterol on fungal cell membranes. It acts as an antifungal agent by causing impaired cell membrane permeability. Damage to the cell membrane is also responsible for the toxicity of amphotericin B. However, it binds to human cell membranes much weaker than to fungal cell membranes.
3. Ergosterol Synthesis Inhibitors : 14-α-sterol demethylase is a microsomal enzyme. It will be inhibited by triazoles to reduce the synthesis of ergosterol and play an antifungal effect. Squalene cyclooxygenase will be inhibited by squalene epoxidase inhibitor to reduce the synthesis of lanosterol (the precursor of ergosterol) and play an antifungal effect.
4. Fungal Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors : Fungal cells convert pyrimidine antifungals to 5-fluorouracil. It inhibits the nucleic acid synthesis of fungi and thus acts as an antifungal agent.
Which fungal infections can they treat?
Flucytosine has strong antagonism against Candida and Cryptococcus. However, since fungi will rapidly develop drug resistance to flucytosine, flucytosine is mainly used in combination with amphotericin B in the clinical treatment of severe fungal infections.
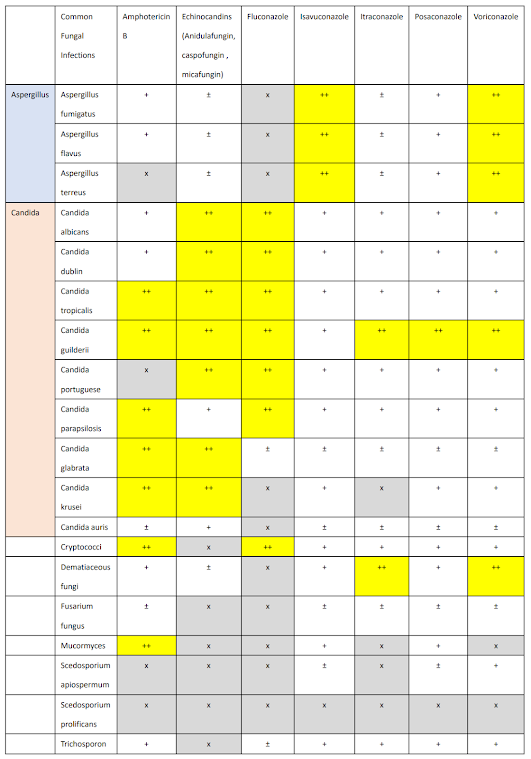
The following table shows the antibacterial spectrum of commonly used antifungal drugs:
How to choose antifungal drugs?
The clinical selection of antifungal drugs is mainly based on the antifungal drug spectrum, pharmacokinetic characteristics, and the severity of the patient's infection. Fluconazole, flucytosine, and voriconazole cross the blood-brain barrier in patients. More than 80% of the dose of fluconazole and flucytosine will be excreted through the kidneys in their original form. Caspofungin, isavuconazole, itraconazole, micafungin, posaconazole, voriconazole, less than 2% of the dose will be excreted unchanged through the kidneys.
1. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis : For patients with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, voriconazole is the first choice for clinical treatment. Isavuconazole will be used as an alternative drug.
2. Candidal disease : Caspofungin or micafungin are the first choice for the treatment of blood infection candidiasis. Since most of the fluconazole taken will be excreted through the kidneys in its original form, fluconazole is the first choice for the treatment of patients with urinary tract infection candidiasis. Amphotericin B can be used as an alternative treatment drug.
3. Cryptococcal disease : For patients with nonmeningitis infections, fluconazole is the first choice for the treatment. In severe cases, amphotericin B can be used for treatment. However, if the patient has meningitis, a combination of amphotericin B and flucytosine is required. When the patient enters the treatment maintenance period, fluconazole can be used. This is due to the fact that both fluconazole and flucytosine can enter the cerebrospinal fluid.
4. Mucormycosis : Clinically, amphotericin B is the first choice for the treatment of patients with mucormycosis. Isavuconazole can be used as an alternative treatment drug.









0 comments:
Post a Comment
Welcome to leave your comment.٩(⚙ᴗ⚙)۶